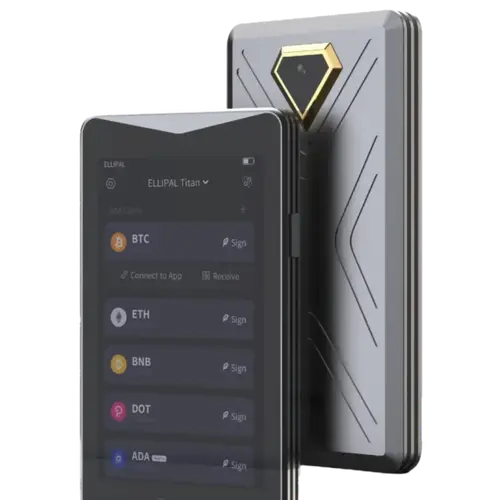

Ellipal
Titan 2.0
Launch Year: 2023
$5 discount with coupon code 'thebitcoinhole'
Summary
Size & Materials: 140g / 4.93oz, 118 x 66 x 9.7 mm, Weather Resistance (IP65)
Display: IPS, Color Screen, Touch Screen, 4"
Input: Touch Screen, Qwerty Keyboard
Power: Battery, USB charging (USB-C)
Security: 100% Air-gapped, Secure Element, Supply Chain & Physical Attacks Protection
Networks: Bitcoin Mainnet, Alt Coins
Firmware: Upgradable Firmware, Upgrade via MicroSD Card
Device Lock: PIN Lock (On Device), Dummy/Decoy/Duress Wallet, Countdown to Brick/Reset PIN, Alphanumeric PIN, Pattern Lock (On Device)
Private Keys: Multiple Private Keys, Passphrases support (BIP-39)
Address Format: Legacy (P2PKH), Nested Segwit (P2SH)
Signing Connectivity: Sign via QR
Fees: Fee Control
Price History
Loading price history...
| Brand | Ellipal |
|---|---|
| Headquarters / Location | |
| Website | https://www.ellipal.com/ |
| Blog | https://www.ellipal.com/blogs/news |
| X (Twitter) | @ellipalwallet |
| YouTube | @ellipal3906 |
| GitHub | ELLIPAL |
| Telegram | - |
|---|---|
| ELLIPAL_Official |
Official Store
PO Box Support
?
BTC On Chain Support
YES (via Crypto.com Pay or Coinbase Commerce)
BTC Lightning Support
NO
Alt Coins Support
YES (via Crypto.com Pay or Coinbase Commerce)
Credit/Debit Card Support
YES
Size & Materials
Hardware wallet warranties typically cover defects in materials and workmanship for a specified period after purchase. These warranties vary by manufacturer and product, so it's essential to understand the terms and conditions before purchasing a hardware wallet.
Some manufacturers decide to sell their product 'as is'. This is a term commonly used in the context of sales transactions, indicating that the product is being sold in its current condition, without any warranties or guarantees from the seller. It essentially means that the buyer is accepting the item in its current state, with all its potential flaws and issues, and the seller is absolving themselves of responsibility for any defects or problems that may arise after the sale.
1 year
Weight and dimensions could be important considerations when choosing a hardware wallet, but their significance depends on your specific needs and preferences. A lightweight and compact hardware wallet is generally more portable and convenient to carry in your pocket. But you are not going to have all your life savings' keys in your pocket, so weight and dimensions should only matter you when you are going to use the wallet for small funds on a daily basis.
140g / 4.93oz
Length x Width x Height
- Length: the longest side of the device
- Width: the shorter side of the device
- Height: the vertical dimension of the device
118 x 66 x 9.7 mm
The materials used in a hardware wallet are of significant importance as they directly impact the device's durability, security, and overall quality.
The materials determine how resistant the hardware wallet is to wear and tear, physical damage, and environmental factors. High-quality, durable materials can ensure the wallet withstands everyday use, drops, and potential exposure to moisture or extreme temperatures.
The materials can influence the physical security of the device, including protection against tampering or unauthorized access attempts. Robust materials can make it more difficult for attackers to physically manipulate or compromise the wallet's security.
Metal
Available in colors
NO
The importance of a hardware wallet being Weather Resistant primarily relates to the device's durability and resilience against potential environmental hazards. Accidents happen, and devices can be exposed to liquids unintentionally. A Weather Resistant hardware wallet can safeguard your bitcoin in case of spills, rain, or accidental immersion.
Devices are typically rated using the Ingress Protection (IP) scale, which indicates the level of protection against dust, solid particles, and moisture.
An IP rating (Ingress Protection rating) is a standardized way to describe how well a device is protected against solids (like dust) and liquids (like water). The rating consists of two digits:
- The first digit represents protection against solid particles (e.g., dust).
- The second digit represents protection against liquids (e.g., water).
First Digit (Protection Against Solids):
- IP0X: No protection against solid objects.
- IP1X: Protection against solid objects larger than 50 mm (e.g., accidental touch by hand).
- IP2X: Protection against objects larger than 12.5 mm (e.g., fingers).
- IP3X: Protection against objects larger than 2.5 mm (e.g., tools or thick wires).
- IP4X: Protection against objects larger than 1 mm (e.g., thin wires or small tools).
- IP5X: Dust-protected. Limited ingress of dust is allowed, but it won't interfere with operation.
- IP6X: Dust-tight. Complete protection against dust, ensuring no ingress of particles.
Second Digit (Protection Against Liquids)
- IPX0: No protection against water.
- IPX1: Protection against vertically falling water droplets (e.g., light rain).
- IPX2: Protection against vertically dripping water when tilted up to 15°.
- IPX3: Protection against water sprayed at an angle of up to 60° (e.g., light splashing).
- IPX4: Protection against water splashes from any direction.
- IPX5: Protection against water jets from any direction (e.g., a garden hose).
- IPX6: Protection against powerful water jets (e.g., heavy rain or washing with a hose).
- IPX7: Protection against temporary immersion in water up to 1 meter deep for up to 30 minutes.
- IPX8: Protection against continuous immersion in water beyond 1 meter.
IP65
Official Documentation
Display
It is crucial to protect yourself against manipulation and malware by verifying transaction details on a dedicated device, preferably different from the device where you generated the transaction. Transactions are often created on desktops, laptops, or mobile phones, which have large attack surfaces and are difficult to secure completely against malware.
Clipboard malware and other types of malicious software may attempt to manipulate your transaction data to redirect funds to an attacker. This is why most hardware wallet devices have dedicated screens to display transaction details. The earliest hardware wallet devices lacked these screens, so users would blindly sign transaction data without being able to verify it. This approach left users vulnerable to man-in-the-middle malware attacks.
By using a dedicated device with a built-in screen for transaction verification, you can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to malware that tries to manipulate your transactions.
In a multisig setup, while having a display on each hardware wallet can provide additional verification, it is not strictly necessary for every device to have one. The primary goal is to ensure that the appropriate number of participants with their corresponding private keys participate in the signing process. The key benefit of a multisig scheme is that it distributes trust among multiple parties and reduces the risk of a single point of failure. By requiring multiple signatures, the scheme ensures that a single compromised device or key is insufficient to authorize a transaction. This setup provides enhanced security, even if not all hardware wallets have a display for transaction verification.
YES
Screen Type
IPS
Gorilla Glass
NO
Color Screen
YES
Touch Screen
YES
A larger screen with higher resolution can display transaction details, including sender and recipient addresses, amounts, and transaction fees more clearly, reducing the risk of human error during verification.
Many hardware wallets use QR codes for transaction information exchange. A larger screen makes it easier to scan QR codes accurately.
4"
Screen Resolution
?
Input
Controls
Touch Screen
Qwerty Keyboard
YES
Power
A hardware wallet with a built-in or removable battery allows for greater mobility and independence from a computer or other power source. Also, a hardware wallet with a battery can reduce the risk of potential attacks related to compromised or malicious USB ports on computers.
YES
Removable batteries make it easier to replace a worn-out or failing battery when it reaches the end of its life cycle. This can extend the overall lifespan of the hardware wallet, potentially saving the user from having to replace the entire device.
Users can keep spare, fully charged batteries on hand as backup power sources. This can be especially useful when traveling or in situations where access to charging is limited.
NO
Battery Size
1400 mAh
USB charging
USB-C
Wireless charging offers the convenience of simply placing the wallet on a compatible charging pad without the need for physical connections. This can streamline the charging process and make it more user-friendly.
NO
Security
100% air-gapped hardware wallets can sign transactions, create/restore a wallet and upgrade the firmware without connecting the device to a cellular network, wifi, Bluetooth, USB, or NFC. This guarantees you that your private keys never touch the internet.
Most fully air-gapped wallets use scannable QR codes for transactions, though some may also use micro-SD cards.
YES
Official Documentation
A hardware wallet is considered a safer option for holding Bitcoin compared to software wallets on desktop or mobile devices, which are more susceptible to remote attacks and malware. However, even a hardware wallet is not immune to physical attacks if it falls into the wrong hands. This is where a secure element chip can provide added protection by preventing physical attacks on the wallet.
A secure element is a microprocessor that separates, keeps, and secures sensitive information, like your private keys. It offers a superior level of protection against physical breaches compared to a mobile phone, desktop, or laptop. This makes it harder for the device to be compromised through fault attacks, side-channel attacks, and cold boot attacks.
But we need to take into account that secure elements are proprietary and closed-source chips and are subject to non-disclosure agreements (NDAs). Some hardware wallets are including more than one secure element to reduce the trust in a single manufacturer. While secure elements provide an added layer of protection, they can increase the cost of hardware wallets and restrict users from creating their own devices.
So, as you can see there are some pros and downsides to using a secure element. They are generally considered a useful way to add an extra layer of security to protect devices from various types of attacks. But no having a secure element is not a big deal if you use a passphrase. A Passphrase is an optional feature of some wallets that serve as a function of second-factor protection of the recovery seed and are an ultimate protection against attacks involving physical access to the device or the recovery seed. Using a passphrase guarantees you that even if after a physical attack, someone can access your private keys from the wallet, they will still need your passphrase to see or spend your funds.
YES (EAL 5+)
Before a hardware wallet gets into your hand, many people might have handled it before you. These people can include the shipping company, the retailer, the shipping person, and many more. If anyone of them is a hacker, they can modify the hardware wallet, install some malware, put it back together, and ship it to you. Some manufacturers protect you against these supply chain attacks using different approaches:
- Deleting the whole system if they detect a breach. A complete deletion gets rid of the private key, meaning there will be nothing left for the hacker to salvage.
- Verification of Authenticity: Utilizing cryptographic signatures to sign the firmware and software loaded onto the hardware wallets. This helps users verify the authenticity and integrity of the device's software.
- Secure Packaging and Sealing: Implementing tamper-evident packaging and sealing mechanisms to make it evident if a device has been opened or tampered with during transit.
- Secure Boot: Implementing a secure boot process that ensures only verified and signed firmware can be loaded onto the device.
- Firmware Updates Verification: Requiring firmware updates to be digitally signed and verified before installation to prevent unauthorized changes to the device's software.
- Shipping wallet without firmware installed to ensure that you install an authentic and the most recent firmware version.
YES
To ensure the highest level of security, it's essential to use hardware that adheres to established security standards for nonce generation. One such standard is RFC6979, which specifies the use of deterministic nonces. Unlike traditional nonces, which are randomly generated, deterministic nonces are calculated in a predictable and repeatable way based on the transaction data and private key. This predictability ensures that the same nonce is always generated for the same data, eliminating the risk of generating a weak or reused nonce.
Why is this important? Nonces play a pivotal role in securing your private keys during the transaction signing process. If a nonce is reused or improperly generated, it can expose your private key, making your Bitcoin vulnerable to theft. By using hardware that follows RFC6979, you can significantly reduce the risk of such vulnerabilities. This standard ensures that nonces are generated in a secure and deterministic manner, effectively safeguarding your Bitcoin from cryptographic attacks.
?
Hardware wallets use private keys to create digital signatures that authorize transactions. These signatures are mathematically constructed with a nonce, which is a secret number chosen by the hardware wallet. However, a malicious hardware wallet can potentially leak private keys through manipulated nonces. To prevent this, a nonce contribution from the host software can be included to provide added security for the user’s funds.
The anti-klepto protocol can safeguard against this type of attack by allowing a computer or mobile wallet to verify the integrity of signatures and take action if any manipulation is detected.
NO
Networks
Mainnet is the term for the real Bitcoin blockchain, and is used in contrast with testnet, signet, and regtest networks. Unlike the other networks, which are used for testing purposes, mainnet coins (BTC) have monetary value. When people refer to the Bitcoin network, they are usually referring to mainnet.
YES
Testnet is an alternative Bitcoin blockchain specifically designed for testing purposes. It is a sandbox environment that allows developers, users, and businesses to experiment with new features, applications, and ideas without risking real Bitcoin or disrupting the main Bitcoin network (mainnet). The Testnet is a valuable tool for the Bitcoin community because it enables the development and testing of new technologies, improvements, and features before they are implemented on the mainnet.
NO
For bitcoin only users, a hardware wallet not supporting alt coins is a key feature. Less code means less attack surface which further improves your security when only storing Bitcoin.
YES
Official Documentation
Firmware
Bitcoin-only firmware only supports the Bitcoin network. Less code means less attack surface which further improves your security when only storing Bitcoin.
If you are a Bitcoiner, you probably want a BTC-only hardware wallet, or at least one where you can install BTC-only firmware. If you also want to store altcoins, then you need to take a look at the list of tokens supported by the wallet.
NO
Firmware upgrades often include security improvements that address newly discovered vulnerabilities or potential attack vectors. By staying up-to-date with the latest firmware, you can ensure that your hardware wallet is secure, protecting your bitcoin.
Offline updates via SD card provide key safeguards:
- Your device is isolated from the internet during updates. Your keys cannot be extracted remotely.
- Secure data transmission via the SD card ensures a strict one-way flow to the device. Nothing leaves your device.
Even if data were somehow transmitted from your device to the SD card, the wallet manufacturer has no ability to access or interact with users' SD cards.
Other approaches, like upgrading the firmware using USB data or Bluetooth are less secure, because they are two-way flows, so the keys could potentially be extracted by the companion app
YES
Upgrade via MicroSD Card
YES
Upgrade via USB External Storage
NO
Upgrade via USB Cable
NO
Upgrade via Bluetooth
NO
Upgrade via NFC
NO
Secure Boot is a technology that prevents unsigned boot firmware from running on your device, such as a compromised firmware image from an attacker.
?
Latest Version
?
References
- Green: less than 6 months old
- Yellow: between 6 months and 1 year old
- Red: more than 1 year old
?
A hardware wallet with source-available firmware is released through a source code distribution model where the source can be viewed, and in some cases modified, but without necessarily meeting the criteria to be called open-source. Any firmware is source-available as long its source code is distributed along with it, even if the user has no legal rights to use, share, modify, or even compile it. These hardware wallets allow users to review the source code, ensuring transparency and trust in the device's operations. Users can examine how the wallet handles their sensitive information and verify that it aligns with their expectations. The availability of the source code also facilitates security audits by independent experts and the broader community. This scrutiny helps identify vulnerabilities or weaknesses in the wallet's design, enabling timely fixes and improvements to enhance overall security.
NO
A hardware wallet firmware being Free and open-source software (FOSS) means that the source code of the firmware is publicly available and can be freely viewed, used, modified, and distributed by anyone. Users have the legal rights to access, study, modify, and distribute the firmware according to the terms of the open-source license it is released under. This transparency and freedom allow the community to review and contribute to the development of the firmware, ensuring its security, reliability, and trustworthiness.
NO
Open source licenses grant permission for anybody to use, modify, and share licensed software for any purpose, subject to conditions preserving the provenance and openness of the software.
-
Whilst anyone may inspect the source code of free and open source software for malicious flaws, most software is distributed pre-compiled with no method to confirm whether they correspond.
A build is reproducible if given the same source code, build environment and build instructions, any party can recreate bit-by-bit identical copies of all specified artifacts.
NO
Device Lock
An access PIN helps ensure that only the owner can immediately access the key signing capability on the device. Usually, entering the incorrect PIN repeatedly results in a delay that increases with each mistake.
Support for entering the PIN directly on a hardware wallet is crucial for ensuring the security of your wallet. Hardware wallets provide an extra layer of security by allowing users to enter their PIN directly on the device itself. This eliminates the risk of keyloggers, which are malicious software or hardware designed to record keystrokes on a computer or smartphone. By entering the PIN on the hardware wallet's physical buttons or touchscreen, you ensure that the PIN remains secure and cannot be intercepted by any malware on your computer.
Additionally, hardware wallets may have mechanisms in place to detect and prevent brute-force attacks, where an attacker repeatedly guesses the PIN to gain unauthorized access.
Given that hardware wallets can be used offline, disconnected from any internet-connected devices. This offline functionality ensures that your PIN remains private and cannot be compromised by any online threats.
On Device
This feature randomizes the numbers associated with the buttons on the keypad. Cameras and shoulder-surfers watching won't figure out your PIN based on the keys you press.
NO
To prevent against brute-forcing the PIN, some hardware wallets can brick or wipe the device after entering a wrong PIN if the maximum number of attempts is exceeded.
YES
Official Documentation
If an user try to unlock with the wrong pin five times, a warning is displaying. If the user use the wrong pin ten times, everything in the device is deleted.
The Brick/Reset me PIN is a special PIN that will tell the device to destroy/wipe itself once entered.
NO
As a defensive measure, this feature can force a time delay when logging into the wallet.
NO
Anti-phishing words are a set of words unique to the device and the PIN introduced. If a user enters the first part of their PIN and does not see their usual anti-phishing words, they know the device is not trustworthy and shouldn't continue the login process.
NO
Alphanumeric PINs allow for a larger pool of possible combinations compared to numeric-only PINs. This increased complexity makes it more difficult for an attacker to guess or brute-force the PIN, providing better protection against unauthorized access.
Alphanumeric PINs can also help protect against shoulder surfing attacks, where an attacker tries to observe and memorize the PIN being entered. The inclusion of letters and symbols in the PIN makes it harder for an attacker to accurately remember the sequence of characters.
YES
A pattern lock is a type of security measure commonly used on touchscreen devices, to restrict unauthorized access. It involves drawing a specific pattern by connecting a series of dots or nodes displayed on the screen.
It may not be as safe as other locking methods for several reasons:
- Predictable Patterns: Many users tend to create simple and easily guessable patterns, such as a straight line, a simple shape, or a letter of the alphabet. These patterns can be relatively easy for someone with malicious intent to guess through trial and error.
- Residue Marks: Over time, the repeated swiping of fingers on the screen can leave residue marks or smudges, which can give visual cues to an attacker about the pattern used, making it easier to guess.
- Shoulder Surfing: An attacker could potentially watch you input your pattern from a distance, especially in crowded or public places. Unlike a PIN or password, a pattern can be observed visually, making it susceptible to shoulder surfing attacks.
While pattern locks may offer a convenient way to unlock a device, especially for quick access, it's essential to balance convenience with security. To enhance the security of your device, consider using longer and more complex PINs or passwords and being cautious about where and how you input your pattern in public settings.
On Device
A fingerprint lock, also known as fingerprint authentication or fingerprint recognition, is a security feature that uses an individual's unique fingerprint to verify their identity and provide access to the wallet.
There are some reasons why fingerprint locks may not always be considered completely safe:
- False Positives and Negatives: Fingerprint recognition systems can sometimes produce false positives (accepting an unauthorized fingerprint) or false negatives (rejecting an authorized fingerprint). These errors can result from factors such as poor fingerprint quality, changes in skin conditions, or variations in finger placement.
- Spoofing and Forgery: Advanced attackers may attempt to create a fake fingerprint (a fingerprint forgery) or use a high-resolution photograph of a fingerprint (a fingerprint spoof) to fool the recognition system. Some biometric systems are more resistant to these attacks than others, but no system is entirely immune.
- Database Vulnerabilities: Storing fingerprint data in a centralized database can pose security risks. If the database is compromised, attackers may gain access to users' fingerprint templates, which could potentially be used for malicious purposes.
- Unauthorized Access: If someone has access to your finger when sleeping, they could potentially unlock your device without your consent or knowledge. This includes family members, friends, or anyone who can physically access your finger while you sleep.
NO
A dummy/decoy/duress wallet is a wallet that contains a smaller amount of funds, to protect against coercion or theft.
The $5 wrench attack is a threat where an attacker may use physical force, such as violence or coercion, to force someone to reveal their private keys or passwords. To mitigate this risk, users might employ plausible deniability strategies.
Hardware wallets offer different ways to generate dummy wallets:
- Some wallets offer a duress PIN, which is an additional PIN that can be used in situations where a user is forced to access their wallet under duress or coercion. The duress PIN functions differently from the regular PIN used to access the hardware wallet. While the regular PIN grants full access to the wallet's funds and features, the duress PIN is designed to appear as a normal PIN but actually provides access to a separate, predetermined dummy wallet or a subset of funds that the user has designated.
- Other wallets offer a single PIN but multiple accounts protected by different passwords, so you can store multiple private keys. Some of those accounts can be used as dummy wallets.
YES
Official Documentation
Setup alternate accounts that shows up when the wallet is unlocked with your alternate password if you are being threatened.
Private Keys
A stateless (or ephemeral) signing device does not store any wallet information (like your private keys) and requires manual input of a recovery seed phrase upon every session. Some users prefer stateless signing because there is nothing of value to steal from the locked device.
NO
Hardware wallets generate seed phrases by creating a seed, which is then usually translated into a list of 2048 words. Various techniques are employed to ensure randomness (known as entropy), such as the usage of random number generators (RNGs). In many hardware wallets, the RNG firmware is executed on an isolated microprocessor known as a secure element, which is embedded in the physical hardware wallet. Other wallets use a combination of internal and external sources to generate entropy, and rolling dice is a common example of the latter.
When creating your own keys, there are many ways to do it, since we just need a very long random number. Sadly, people aren't good at making random numbers. This is why brain wallets, which use phrases from songs, books, or poems, aren't safe. If you use a popular phrase for a brain wallet and send money to it, you'll lose the money quickly.
To make a truly random number, one way is to use high-quality dice, like those found in casinos. Roll them several times to create a long random number. Some hardware wallets have the option to enter dice rolls directly on the device to create a seed phrase.
NO
Support to store multiple persistent private keys on the device.
YES (10)
A passphrase is an advanced feature that can be used to protect your accounts. When this feature is enabled, your device asks you to enter a secret phrase in addition to your numeric PIN every time you connect your device. When you enter a passphrase, your device combines the already existing randomness of your seed phrase with your own chosen passphrase and computes a new wallet.
There is no such thing as an 'incorrect passphrase' and you can create an unlimited number of wallets. This can be quickly turned to your benefit when you decide to redistribute your balances to give you a 'cover'.
You could consider leaving some pocket change, funds you would use for smaller everyday purchases, on your unprotected account (just the PIN, no passphrase). Then, move a moderate chunk of your savings under a passphrase of your choosing. Lastly, you can move the greater part of your balance to a completely different passphrase. In a situation where you are physically threatened by burglars, border security agents, or pretty much anyone else, you can now safely give up your PIN number. If the assailants keep you under duress and demand a passphrase, you can give out the one with the lesser amount.
As a plus, using passphrases can also add an extra security layer when some exploits are found on a hardware wallet.
Another advantage of using passphrases is that they help to increase the security of your seed phrase backups. If you use a passphrase, you can locate your seed phrase in one place and your passphrase in another different location. So, if someone finds any of them, they won't be able to access your funds.
YES
Some hardware wallets typically have minimal buttons, making it quite challenging to input a BIP-39 optional passphrase. To simplify the passphrase entry process, they enable users to enter the passphrase on the host device, which then transfers it to the hardware wallet. This approach compromises some of the security benefits of using a passphrase since the host device learns the passphrase, which is part of your backup. However, it also exposes users to a more severe attack:
A manipulated passphrase is sent to the hardware wallet. When entering your passphrase on a malicious host device, an attacker could secretly transmit a different passphrase to your wallet. Everything will appear to function normally until you attempt to make a transaction. The attacker can then hold your coins for ransom and might only give out the correct passphrase after you have paid them.
Always use a hardware wallet that allows you to input your passphrase directly on the device. As a result, the host device never gains access to the passphrase or can manipulate it.
On Device
The Master Key Fingerprint refers to the fingerprint of the master extended public key derived from a hierarchical deterministic (HD) wallet.
The master extended public key (xpub) is derived from the master extended private key (xprv) and can be used to generate a series of child public keys. The fingerprint, in this case, is a unique identifier derived from the hash of the parent key's public key. It helps in quickly identifying the corresponding master key within a hierarchical key structure.
The fingerprint is unique and it is represented by 8 characters, for example 91A876EF
When you add a passphrase to your seed phrase, the new wallet will have its own fingerprint. This fingerprint can be used to verify that you have entered your passphrase correctly, that's why is important that your hardware wallet displays it.
NO
BIP-85 is a Bitcoin standard that introduced a process to mathematically derive multiple seeds from the value of just one seed. The derived seeds are unique and cannot be traced back to one another, nor can they be traced back to the original seed value.
NO
Shamir's secret sharing (SSS) is a cryptographic technique formulated in 1979 by the Israeli cryptographer Adi Shamir. The essence of Shamir's scheme lies in the ability to back up, share and recover a secret by breaking up the secret into multiple shares that are individually useless and leak no information about the secret or the scheme setup.
You can choose how many recovery shares you want to generate, and decide how many of them you want to use for recovery. Individual shares do not leak any information about the shared secret, as long as the number of compromised shares does not reach the required threshold. For example, if you use a 3-of-5 scheme and 2 of your shares get compromised, the attacker has no chance to reconstruct your wallet and cause trouble.
NO
Seed XOR is a technique that consists of storing secrets in 2, 3, or 4 parts that look and behave just like the original secret. One 24-word seed phrase becomes two or more parts that are also BIP-39 compatible seed phrases. These should be backed up in your preferred method, metal or otherwise. These parts can be individually loaded with honeypot funds as each one is 24 words, with the 24th being the checksum and will work as such in any normal BIP-39 compatible wallet.
NO
Some hardware wallets provide support to backup the seedphrase on a microSD card. It's important to mention that encrypted backups is an additional security measure that can provide enhanced protection.
NO
Some hardware wallets provide support to backup the seedphrase on a NFC card.
NO
12 Words BIP-39 Seed Creation
NO
24 Words BIP-39 Seed Creation
YES
12/24 BIP-39 Words Display
On Device
12 Words BIP-39 Seed Import
On Device
24 Words BIP-39 Seed Import
On Device
SeedQR is a standard developed by SeedSigner for encoding a recovery phrase as a human-transcribable QR code. It is another way to store a recovery phrase, as a QR code instead of a list of 12 or 24 words.
NO
Key Teleport is a feature that lets you securely transfer:
- Seed phrases (words, xprv)
- Secure notes/passwords (singular or all in vault)
- Partially signed Bitcoin transactions (PSBTs) for multisig
NO
Address Format
Pay-to-Public-Key-Hash (P2PKH): Addresses starts with '1'. This is the most common script type used in Bitcoin transactions. In a P2PKH transaction, funds are sent to the hash of the recipient's public key. To spend these funds, the recipient must provide a signature that matches the public key.
YES
Pay-to-Script-Hash (P2SH): Addresses start with '3'. From this format, we can't distinguish whether they are MultiSig addresses or Segregated Witness compatible addresses. P2SH is the abbreviation of “Pay To Script Hash” and it supports more than Legacy Functions with more complex formats , such as specifying multiple digital signatures to authorize transactions.
YES
Pay-to-Witness-Public-Key-Hash (P2WPKH also known as Bech32): Addresses starts with 'bc1'. Using a wallet that supports native SegWit is beneficial since it offers improved security and faster transaction times while keeping fees low.
NO
Pay-to-Taproot (P2TR also known as Bech32m): Addresses start with 'bc1p'. It offers improved privacy when transacting on the Bitcoin network.
NO
Receive Addresses
Support to view the receive address as a text
On Device
Support to view the receive address as a QR code
On Device
Export Address to SD Card
NO
Support to scan a QR with a receive address and verify if it is part of the wallet
?
Signing
Bitcoin multi-sig allows having up to 15 possible signers to approve any transaction. When using multi-sig, you will have at least one seed phrase per signer, so you can store them in multiple locations.
One reason multi-signature wallets are secure is their built-in redundancy. This assumes you don't store all the keys in the same place, like a drawer in your office. Instead, you should distribute the keys across different locations. This protects you from various threats and potential losses. For example, house fires are more common than people think, so off-site data storage is essential for recovery if something goes wrong.
Storing keys in geographically distributed locations protects you from many different attacks and losses. The further apart they are, the safer it is. However, keep in mind that greater distances can make it less convenient to access your keys.
Using multiple brands of hardware wallets in a multisig setup for Bitcoin is important for several reasons. Primarily, it enhances the security of your funds by reducing the chances of a single point of failure. Each brand of hardware wallet has its own design, architecture, and security implementations. By using different brands, you reduce the risk of your entire multisig setup being compromised if a vulnerability is discovered in one specific hardware wallet model or brand. Multisig setups with multiple brands of hardware wallets can better protect you from supply chain attacks or targeted attacks on a specific wallet brand. In the event that one of the wallet brands is compromised at the manufacturing or distribution level, your funds remain secure because the attacker would still need to compromise the other wallet brands in your multisig setup. Finally, trusting a single manufacturer means relying 100% on their hardware security practices and their good intentions.
NO
FROST (Flexible Round-Optimized Schnorr Threshold Signatures) is a protocol that minimizes the number of rounds of communication between participants in Schnorr signature schemes, reducing network bandwidth, time, and probability of errors. It requires a maximum of three rounds for signing, even without a trusted signature aggregator or preprocessing stage. It can be used to implement 'n-of-m' threshold signatures represented by a single signature on the blockchain. This saves block space and increases privacy by making them indistinguishable from other, more common spend types.
NO
This feature allows single-tap broadcast of the freshly-signed transaction.
Once enabled with a URL, the device will show the NFC animation after signing the transaction. When the user taps their phone, the phone will see an NFC tag with URL inside. That URL contains the signed transaction ready to go, and once opening in the mobile browser, that URL will load. The landing page will connect to a Bitcoin node (or similar) and send the transaction on the public Bitcoin network.
NO
Message signing is the process of using your wallet's private key to create a cryptographic signature for a specific message. This proves that you control the Bitcoin address without exposing your private key or spending any coins.
NO
Change verification is a security feature that helps prevent a type of attack where the wallet sends your leftover coins (the change) to an address controlled by an attacker, instead of back to you.
Without change verification, a compromised wallet interface (like a malicious desktop app or web wallet) could:
* Show you a legitimate transaction.
* Secretly send the change to an attacker's address.
You'd still see the correct recipient address and amount, but you'd lose the remaining funds.
?
Change Address Display
?
Signing Connectivity
Some hardware wallets can connect to a computer or mobile device via a USB cable. This wired connection is widely supported and provides a relative convenient way to transfer transaction data between the wallet and the device, although it is not considered the most secure way because it is not air-gapped.
NO
Some modern hardware wallets offer Bluetooth connectivity, allowing them to connect wirelessly to mobile devices and computers. Bluetooth provides convenience and mobility but requires careful security considerations to prevent unauthorized access.
Bluetooth technology has security considerations that need to be addressed when using it for hardware wallets. Secure pairing, authentication, and encryption protocols should be implemented during the pairing process. Man-in-the-Middle attacks can target Bluetooth connections, so encryption and authentication mechanisms should be in place. Bluetooth's limited range provides some protection against remote attacks, but physical access within range could still pose risks. It's important to assess the specific implementation and security measures of a Bluetooth-enabled hardware wallet before relying on it.
NO
Near Field Communication (NFC) is a technology that enables two devices to communicate wirelessly when they are brought close to each other. NFC is often used as a way to quickly and securely (compared with USB or Bluetooth) connect the wallet to a mobile device, such as a smartphone or tablet.
NO
Some hardware wallets have a MicroSD card slot that allows users to transfer data, including transaction information, to and from the wallet using a MicroSD card. This is often used for air-gapped transactions and firmware installation.
NO
A QR scanner on a wallet is a feature that allows you to scan a QR code using your wallet. Users can generate a transaction on an online device, encode it as a QR code, and then sign it securely on the offline wallet.
YES
Official Documentation
Camera: 2.4M AF
URs (Uniform Resources) are a method for encoding structured binary data for transport in URIs and QR Codes.
UR2.0 is the industry standard for airgapped data transmission in Bitcoin.
NO
BBQr enables files larger than can fit into a single QR to be sent as a series of QR codes (sometimes called an “animated QR”). The target file types are PSBT (BIP-174) and signed Bitcoin transactions.
NO
pMofN (Specter) QR
NO
Spending Conditions
Spending Conditions refers to the set of rules that must be met in order to spend a certain output (also known as a UTXO - Unspent Transaction Output).
Caps the amount of Bitcoin that can be spent in a single transaction.
NO
Restricts how fast transactions can occur, requiring a minimum number of blocks between spends.
NO
Only allows to send to pre-approved Bitcoin addresses.
NO
Requires confirmations from a mobile 2FA application.
NO
Miniscript is a scripting language designed for Bitcoin. It aims to provide a more flexible and secure way of defining spending conditions for Bitcoin transactions.
NO
Taproot Miniscript is a high-level language or template system for building Taproot-compatible scripts.
NO
Fees
Fee control in a Bitcoin wallet refers to the ability of the user to adjust the transaction fee associated with sending a Bitcoin transaction. When you send a Bitcoin transaction, you usually include a fee as an incentive for miners to process and include your transaction in the blockchain.
Fee control allows you to choose how much you want to pay in transaction fees. This choice involves a trade-off between the speed at which your transaction gets confirmed and the cost of the fee. Transactions with higher fees are usually processed more quickly by miners because they have a higher incentive to include them in the next block.
YES
Replace-by-fee, or RBF, means that you are replacing one version of an unconfirmed transaction with a new version that pays a higher fee. As a result of increasing the fee, your transaction will now become more attractive to the miners and will have a higher chance of being confirmed faster. Additionally, RBF allows to cancel a pending outgoing transaction and get its value back to wallet.
NO
Child-Pays-For-Parent (CPFP) means that you are making your stuck transaction (the “parent”) more rewarding by sending a second new transaction to be mined with a higher fee (the “child”). The child transaction can only be mined after the parent transaction is confirmed.
NO
The device enforces a safeguard against excessive network fees when signing transactions. It will refuse to sign any transaction where the fee exceeds a user-defined percentage of the transaction amount.
?
Privacy
In your wallet, the Bitcoin balance you see is the sum of smaller units called Unspent Transaction Outputs (UTXOs). Each UTXO has a history that may or may not belong to you. If your wallet automatically chooses which UTXOs to use in a transaction, you could be revealing unwanted information to the recipient or anyone monitoring the blockchain.
On the other hand, if your wallet allows you to view and select UTXOs for transactions, you may not know the source of each one. This makes it difficult to decide which ones are suitable for different transactional situations. By using a wallet that enables UTXO labeling and Coin Control, you can minimize the amount of information shared during transactions.
For example, suppose your wallet contains both KYC and no-KYC Bitcoin. It's best not to combine these sources in a single transaction because it will link the no-KYC Bitcoin to the KYC Bitcoin associated with your true identity. If you label your coins as 'KYC' or 'no-KYC', you can make an informed decision when spending your sats in the future.
NO
For bitcoin to function reliably and securely, it relies on the voluntary participation of thousands of individuals worldwide. Nodes, which make up the bitcoin network and verify transactions and blocks, are crucial to this process. There are many reasons to consider running your own bitcoin node, including personal benefits and the benefits to the security and resilience of the bitcoin ecosystem.
NO
Tor (The Onion Router) aims to make all users look the same, making it difficult for you to be fingerprinted based on your browser and device information. With Tor, your traffic is relayed and encrypted three times as it passes over the Tor network. The network is comprised of thousands of volunteer-run servers known as Tor relays. Connecting to your custom Bitcoin node using Tor can provide a number of benefits for privacy and security.
Tor is an anonymity network that helps to conceal your IP address and online activity from potential eavesdroppers, such as your Internet Service Provider (ISP) or other network intermediaries. By using Tor, you can ensure that your Bitcoin node's IP address is not publicly visible and that your node's traffic is encrypted and routed through multiple servers, making it more difficult for someone to trace it back to you.
Connecting to your node using Tor can help to reduce your reliance on centralized services or intermediaries, such as Bitcoin wallet providers or exchanges. By running your own node and connecting to it using Tor, you can have more control over your Bitcoin transactions and data, and reduce your exposure to potential hacks or data breaches at centralized services.
NO
Silent payments (BIP352) are a type of payment that can be made to a unique onchain address for every payment even though the receiver provided the spender with a reusable (offchain) address. This helps improve privacy.
NO
Other Features
Emulates a disk when the device is connected to a computer/phone
NO
Using a hardware wallet as a password manager is not its primary purpose, but it can be utilized for that functionality to some extent. Hardware wallets are primarily designed for securely storing and managing cryptocurrencies by storing private keys and facilitating transaction signing. However, their security features and offline storage capabilities can be repurposed to store sensitive information like passwords.
NO
Universal 2nd Factor (U2F) is an open authentication standard that strengthens and simplifies two-factor authentication (2FA) by using specialized USB or NFC devices based on a similar security technology found in smart cards.
YES
FIDO U2F is a two-factor authentication method (2FA) developed by the FIDO Alliance.
YES
Some Hardware Wallets can be used as security devices to operate GPG, SSH and age. Instead of keeping your key on your computer and decrypting it with a passphrase when you want to use it, the key is generated and stored on the hardware wallet and never reaches your computer.
NO
Official Apps
Web App
NO
Windows App
NO
MacOS App
NO
Linux App
NO
Chrome Extension
NO
Firefox Extension
NO
Edge Extension
NO
Third-Party Apps / Services
Affordable and easy-to-use security for all your sats | BIP-85, Multisig, Own Node, Hardware Wallet support.
NO
Blockstream Green is an industry-leading Bitcoin wallet that offers you an unrivaled blend of security and ease-of-use.
NO
Radically Simple & Powerful Bitcoin Wallet
NO
A self-custodial, Bitcoin-only wallet designed for low-fee, private payments and long-term cold storage.
NO
Casa helps you secure your crypto without wondering if you're doing it right. Hold your own keys and safely take self-custody today.
Casa protects your bitcoin with multiple keys, each stored in separate places for extra security. If one of your keys is lost or stolen, your assets are still protected and you can still access them.
NO
Securing Bitcoin payments since 2011, Electrum is one of the most popular Bitcoin wallets. Electrum is fast, secure and easy to use. It suits the needs of a wide spectrum of users.
NO
Eliminate single points of failure with their state-of-the-art multisig wallet. Get access to inheritance planning, scheduled payments, emergency lockdown, and much more.
NO
Sparrow is a Bitcoin wallet for those who value financial self sovereignty. Sparro's emphasis is on security, privacy and usability. Sparrow does not hide information from you - on the contrary it attempts to provide as much detail as possible about your transactions and UTXOs, but in a way that is manageable and usable.
NO
Specter Desktop is FOSS free open source software under the MIT license. It exists to empower you, to hold your own keys and follow self sovereign best practices. Your Bitcoin node, on your hardware, paired with your signing devices, creating secure wallets for bitcoin self-custody.
NO
Protect your bitcoin with cold storage that you control and get access to trading, inheritance, loans, and IRAs—all backed by the best support in the industry.
NO
Comparing Bitcoin Hardware Wallets (aka Signing Devices) feature by feature
![BitBox02 Nova Bitcoin-only]() BitBox
BitBoxBitBox02 Nova Bitcoin-only
![Coldcard Mk4]() Coinkite
CoinkiteColdcard Mk4
![Coldcard Q]() Coinkite
CoinkiteColdcard Q
![Jade Plus (Plastic)]() Blockstream
BlockstreamJade Plus (Plastic)
![Keystone 3 Pro]() Keystone
KeystoneKeystone 3 Pro
![Krux]() Self-custody Solutions
Self-custody SolutionsKrux
![Passport Core]() Foundation Devices
Foundation DevicesPassport Core
![SeedSigner]() SeedSigner
SeedSignerSeedSigner
![Trezor Safe 3]() Trezor
TrezorSafe 3
![Trezor Safe 5]() Trezor
TrezorSafe 5
![Trezor Safe 7]() Trezor
TrezorSafe 7
![Arculus]() CompoSecure
CompoSecureArculus
![BC Vault]() Real Security
Real SecurityBC Vault
![BitBox02 Bitcoin-only]() BitBox
BitBoxBitBox02 Bitcoin-only
![BitBox02 Multi]() BitBox
BitBoxBitBox02 Multi
![BitBox02 Nova Multi]() BitBox
BitBoxBitBox02 Nova Multi
![Bitkey]() Block
BlockBitkey
![Cardware]() Cardware Wallet
Cardware WalletCardware
![CoolWallet Go]() CoolBitX
CoolBitXCoolWallet Go
![CoolWallet Pro]() CoolBitX
CoolBitXCoolWallet Pro

































 Support Us on Ko-fi
Support Us on Ko-fi